Generating clear and usable textual descriptions of BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) models is crucial for effective understanding and use of these complex business models. BPMN models contain detailed information about business processes that is not always readily accessible to everyone without additional explanation. This lack of clarity can lead to misunderstandings and inefficiencies when making decisions within multidisciplinary teams. Therefore, there is a need for methods that generate understandable and consistent descriptions for these models.
In his master’s thesis, Faysal explored the challenge of how to automatically generate accurate descriptions of BPMN models. He compared three approaches: a template-based approach, an approach using large language models (LLMs), and a hybrid method that combines elements of both techniques. The template-based approach uses predefined templates to generate text, which provides consistency but sometimes leads to less flexibility and creativity in descriptions. The LLM approach exploits advanced language models to produce contextually relevant and coherent text, although this may result in inconsistency or unnecessary contextual additions. The hybrid approach attempts to combine the advantages of both approaches, with the goal of balancing structure and flexibility.
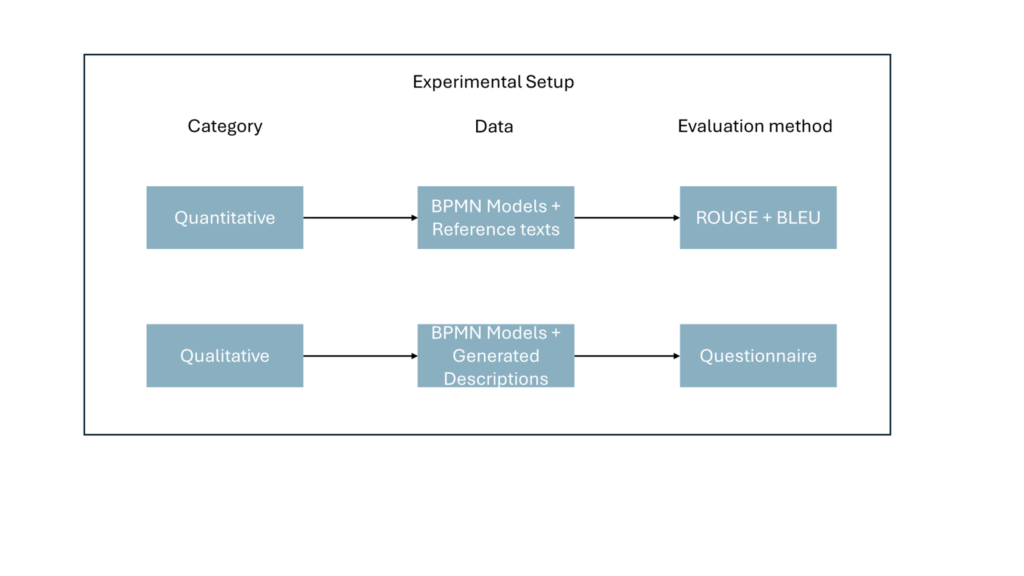
To evaluate the generated descriptions, Faysal used both automatic and human evaluation techniques. Automatic evaluations were performed using the BLEU and ROUGE scores, which measured the accuracy of descriptions by looking at the overlap of words and sentence structures with reference texts. BLEU primarily assesses similarity in n-grams, while ROUGE focuses on how well long word sequences match between the generated and reference descriptions. In addition, an expert survey was conducted in which BPMN experts evaluated the generated descriptions for factors such as readability, grammatical correctness and the extent to which the descriptions matched the BPMN models. This combination of automatic and human evaluations provided multifaceted insight into the quality and usability of the generated textual descriptions.
The survey results provide an overview of the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. The template-based approach proves reliable and consistent, although it is sometimes limited in flexibility. On the other hand, LLM approaches improve the readability and grammatical quality of descriptions, although they may sometimes contain unnecessary contextual additions. The hybrid approach proves effective in combining the advantages of both methods, suggesting that a balanced approach may be the most appropriate solution for different scenarios.
To correctly implement the generated descriptions, it is important to match the chosen method to the specific needs of the project and users. In doing so, it is essential to consider the strengths and weaknesses of each approach so that organizations can make informed choices about which method is most appropriate for generating textual descriptions of BPMN models. This can help improve communication and documentation, making the complexity of business processes more accessible to a wider audience. Faysal’s research provides valuable insights and practical recommendations for improving the textual representation of BPMN models in practice.

Are you interested in writing your thesis with us? Are you excited about the opportunity to be part of PNA’s Data Science & AI team? Learn more about our future projects!